Cold Therapy vs. Heat Therapy
Muscle soreness is a common experience, whether you’ve just finished an intense workout, spent a day tackling household chores, or are recovering from an injury. Understanding how to manage muscle soreness effectively is essential to aid recovery and minimize discomfort. When it comes to soothing sore muscles, two popular methods often come into play: cold therapy and heat therapy. But which is better? The answer depends on the situation, the type of pain you’re experiencing, and your body’s needs.
Understanding Cold Therapy and Heat Therapy
Cold therapy (cryotherapy) and heat therapy are simple, accessible treatments that use temperature to address pain and discomfort. Cold therapy works by reducing inflammation and numbing the affected area, while heat therapy relaxes muscles and improves circulation to encourage healing.
When to Use Cold Therapy
Cold therapy is most effective for acute injuries and inflammation. It works by constricting blood vessels, which reduces swelling and numbs the pain.
Situations Where Cold Therapy is Ideal:
- Acute Muscle Injuries: If you’ve sprained your ankle or pulled a muscle, cold therapy can minimize swelling and discomfort in the first 24–48 hours.
- Inflammation: When muscle soreness stems from inflammation caused by a rigorous workout or overuse, cold therapy can reduce the swelling.
- Post-Surgical Recovery: Many doctors recommend cold therapy for managing pain and swelling after surgery.
How to Use Cold Therapy:
- Ice Packs: Wrap an ice pack in a towel and apply it to the affected area for 15–20 minutes at a time.
- Cold Compresses: Similar to ice packs, these reusable compresses are versatile and convenient.
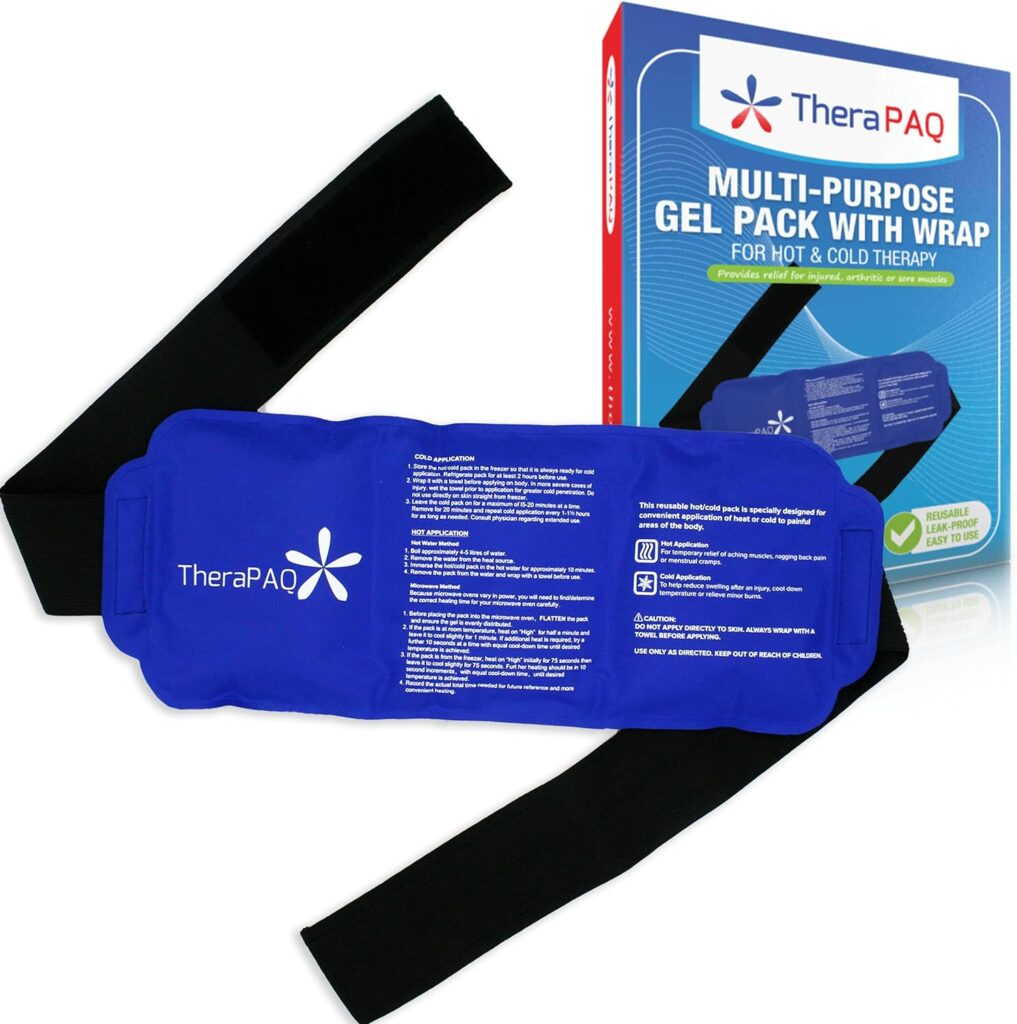
- Cold Therapy Products: Items like the TheraPAQ Reusable Gel Ice Pack or the NatraCure Cold Therapy Wrap are popular on Amazon and highly rated for their effectiveness and durability.
When to Use Heat Therapy
Heat therapy is better suited for chronic pain and muscle stiffness. It works by dilating blood vessels, increasing blood flow, and delivering oxygen and nutrients to the affected area, which promotes healing and relaxes the muscles.
Situations Where Heat Therapy is Ideal:
- Chronic Muscle Pain: If you experience persistent muscle tightness or soreness, heat therapy can help loosen up the muscles.
- Delayed Onset Muscle Soreness (DOMS): When muscle soreness sets in a day or two after exercising, heat therapy can provide relief.
- Stress-Related Muscle Stiffness: Heat therapy is particularly beneficial for tension in areas like the neck, shoulders, or lower back caused by stress or poor posture.
How to Use Heat Therapy:
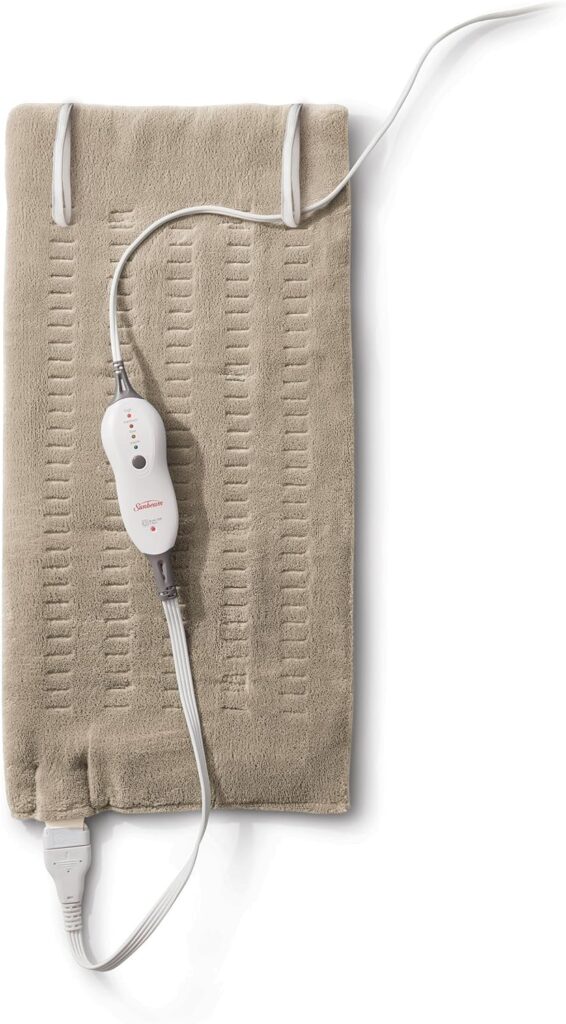
- Heating Pads: Electrical heating pads, such as the Sunbeam King Size Heating Pad, offer adjustable heat settings for targeted relief.
- Hot Water Bottles: These are classic and portable options for heat therapy.
- Warm Baths: Soaking in a warm bath infused with Epsom salts can soothe sore muscles and relax your entire body.
Choosing the Right Therapy for Muscle Soreness
Now that you understand when to use cold therapy and heat therapy, let’s explore how to decide which is better for your specific situation.
Cold Therapy for Immediate Injuries
If you’ve just sustained a muscle injury, such as a strain or sprain, cold therapy should be your go-to. Applying a cold compress or ice pack within the first 24–48 hours helps prevent excessive swelling and reduces pain. For example, if you’re dealing with a pulled hamstring, using a TrekProof Gel Ice Pack can offer immediate relief and help control the inflammation.
Heat Therapy for Stiffness
For muscle tightness or stiffness that has developed over time, heat therapy is more effective. For instance, if your lower back feels sore after sitting at your desk all day, a Pure Enrichment Electric Heating Pad can deliver consistent warmth to ease the tension.
Combining Cold and Heat Therapy
In some cases, alternating between cold and heat therapy can maximize benefits. This is often referred to as contrast therapy and works well for conditions like:
- Tendonitis: Start with cold therapy to reduce inflammation, then switch to heat therapy to encourage healing.
- Chronic Back Pain: If the pain is accompanied by swelling, begin with cold therapy and transition to heat therapy to relax the muscles.
Example:
If you’re experiencing chronic shoulder pain from an old sports injury, apply a cold pack like the Rester’s Choice Gel Ice Pack for 15 minutes, followed by a BESIGILA Large Electric Heating Pad for 20 minutes. This method helps reduce inflammation while promoting blood flow to the area.
Tips for Safe Application
Both cold and heat therapy can be effective when used correctly. However, misuse can lead to skin damage or worsening symptoms. Here’s how to use them safely:
Cold Therapy:
- Avoid Direct Contact with Skin: Always wrap ice packs in a towel to prevent frostbite.
- Limit Duration: Do not apply cold therapy for more than 20 minutes at a time.
- Wait Between Applications: Allow your skin to return to normal temperature before reapplying cold therapy.
Heat Therapy:
- Check the Temperature: Ensure the heating pad or water isn’t too hot to avoid burns.
- Set a Timer: Limit heat application to 20 minutes at a time.
- Avoid Open Wounds: Do not apply heat therapy to areas with cuts or open wounds, as it can increase the risk of infection.
Popular Cold Therapy and Heat Therapy Products
Cold Therapy Products:
Rester’s Choice Gel Ice Pack: Designed for flexibility and long-lasting cold, it’s perfect for sore muscles or injuries.
TheraPAQ Reusable Ice Pack: This versatile pack is great for everything from minor injuries to post-workout soreness.
NatraCure Cold Therapy Wrap: Ideal for knees, shoulders, and other joints, this product is well-rated for its durability and ease of use.
Heat Therapy Products:
Sunbeam King Size Heating Pad: With adjustable heat settings and an extra-large design, this pad is perfect for back pain and larger muscle groups.
Pure Enrichment Electric Heating Pad: Known for its soft fabric and consistent heat, it’s a favorite for daily use.
ThermaCare Heat Wraps: These disposable heat wraps are excellent for on-the-go relief.
When Not to Use Cold or Heat Therapy
While both therapies are generally safe, there are some situations where they should be avoided:
Cold Therapy:
- Poor Circulation: Cold therapy can further reduce blood flow, exacerbating the problem.
- Hypersensitivity to Cold: Conditions like Raynaud’s disease can make cold therapy uncomfortable or harmful.
Heat Therapy:
- Recent Injuries: Heat can worsen inflammation and swelling in the first 24–48 hours after an injury.
- Skin Conditions: Avoid applying heat to areas with rashes or sensitive skin.
Conclusion
Choosing between cold therapy and heat therapy for muscle soreness depends on the nature of your pain and its cause. Cold therapy is ideal for acute injuries and inflammation, while heat therapy works best for chronic pain and stiffness. In some cases, alternating between the two can provide optimal relief.
To ensure effective results, invest in high-quality products such as the Rester’s Choice Gel Ice Pack or the Sunbeam King Size Heating Pad, both available on Amazon and highly rated by users.
By understanding the benefits and applications of each therapy, you can make informed decisions to manage muscle soreness and support your recovery effectively.